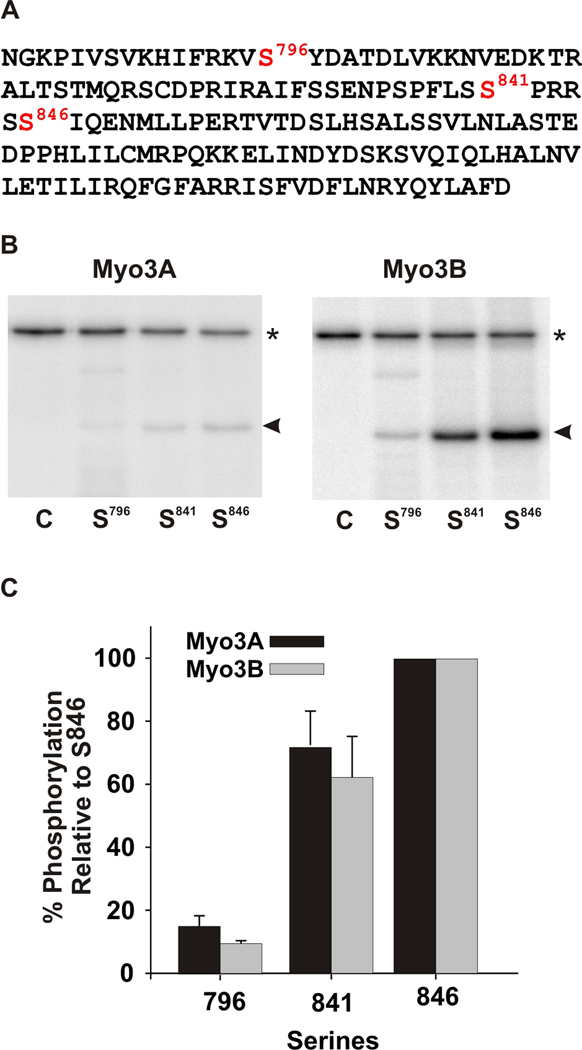
Figure 5. mMyo3A and 3B kinases show similar specificities for predicted PKA and PKC phosphorylation sites in test polypeptide substrates.
A. Wild-type sequence of the test polypeptide, which is the sequence of the loop2 region of the kinase/myosin expressed in Limulus photoreceptors. The sequence contains one predicted PKC phosphorylation site (S841) and two predicted PKA sites (S796 and S846). This sequence was mutated to produce three different substrates in which only one of the three predicted phosphorylation sites was present. The other two serines were converted to alanines. Mutated sequences were expressed in E. coli, purified and incubated together with the mMyo3A and 3B kinases. Kinases were present at 0.4µmol/L; substrates at (1.6 µmol/L). B. Phosphorimages of SDS-PAGE gels which separated the kinases (asterisk) from the substrates (arrow head). The serine available for phosphorylation is indicated below each lane. The control lane (C) contained no substrate. C. Quantification of the phosphorylation of the substrates in three different experiments relative to the phosphorylation of the substrate containing S846 and expressed as the mean % of this phosphorylation ± the standard error of the means.