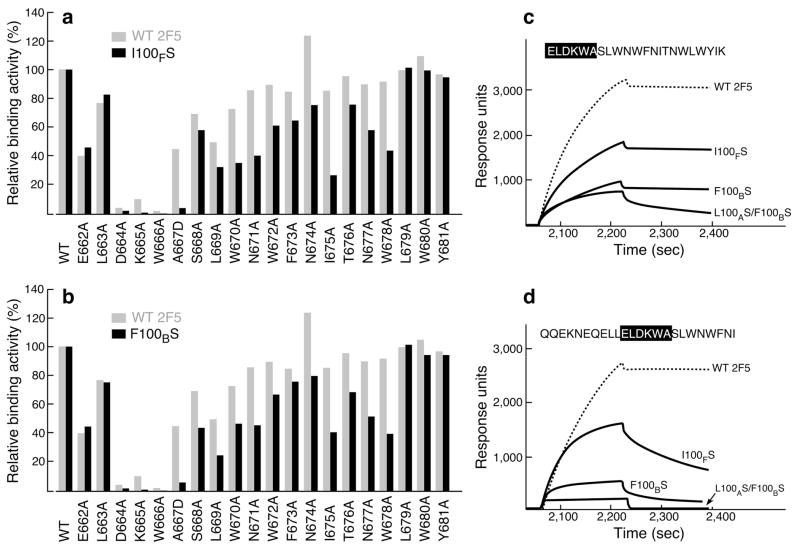
Figure 5. Influence of C-terminal MPER residues on 2F5 and 2F5m binding as measured by SPR.
Each bar represents the apparent I100FS (a) and F100BS (b) binding affinities in comparison with those of 2F5 for a series of alanine-substituted MPER peptides versus wt MPER. For A667, a D substitution was introduced. The amount of each MPER variant peptide bound to DOPC-DOPG liposome was normalized to that of wt peptide. 30 μl of wt 2F5 at 20 μg ml−1, 2F5m I100FS at 35 μg ml−1 and 2F5m F100BS at 50 μg ml−1 were injected over peptide–liposome complex at the flow rate of 10 μl min−1. Apparent binding affinities of each antibody for MPER alanine mutants in comparison with the wt peptide were measured by response units taken on the dissociation time point at 3 min following 3 min of association time by BIAcore. (c,d) Binding of 2F5 and mutants to MPER peptides containing or lacking the C-helical MPER region. 20 μg ml−1 of each antibody was injected over peptide-liposome complex except in the case of double mutant L100AS F100BS where 100 μg ml−1 was used.