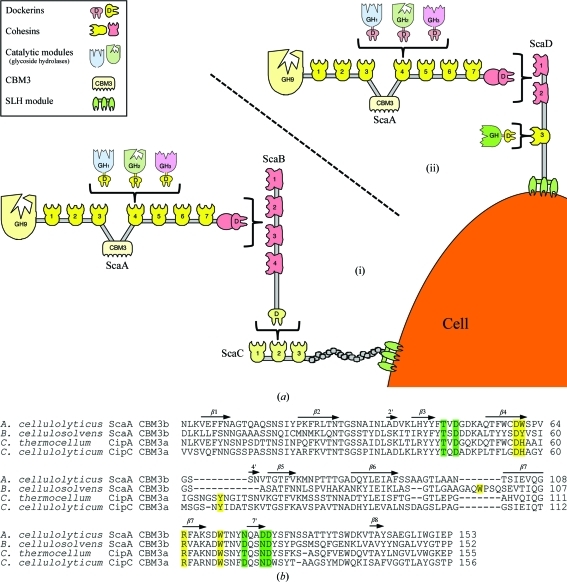
Figure 1.
The scaffoldin-borne family 3b CBM of the A. cellulolyticus cellulosome. (a) Schematic representation of the proposed cell-surface disposition of the cellulosomal components of A. cellulolyticus. The intermolecular cellulosome interactions in this bacterium can be one of two types. (i) Enzyme-borne type I dockerins recognize the type I cohesins of ScaA, the ScaA type II dockerin binds to the type II cohesins of ScaB, the ScaB dockerin binds to the cohesins of ScaC and an SLH module on ScaC serves to attach the entire assembly to the cell surface. (ii) Enzyme-borne type I dockerins recognize the type I cohesins of ScaA and the ScaA type II dockerin binds to one of the two type II cohesins of ScaD. Additionally, a single type I dockerin-containing enzyme binds to the single type I cohesin of ScaD. (b) Sequence alignment of A. cellulolyticus ScaA CBM3b with sequences of other scaffoldin-borne family 3 CBMs: B. cellulosolvens ScaA CBM3b (PDB entry 2xbt; Yaniv et al., 2011 ▶), C. thermocellum CipA CBM3a (PDB entry 1nbc; Tormo et al., 1996 ▶) and C. cellulolyticum CipC CBM3a (PDB entry 1g43; Shimon et al., 2000 ▶). The alignment was performed using ClustalW v.2.0.12 (Larkin et al., 2007 ▶). Secondary-structural elements (β-strands) corresponding to the A. cellulolyticus ScaA CBM3b structure are indicated as arrows and numbered. Proposed cellulose-binding amino-acid residues are shown in yellow. Putative calcium-binding residues are shown in green. The numbering of the A. cellulolyticus ScaA CBM3b sequence is according to the observed electron density.