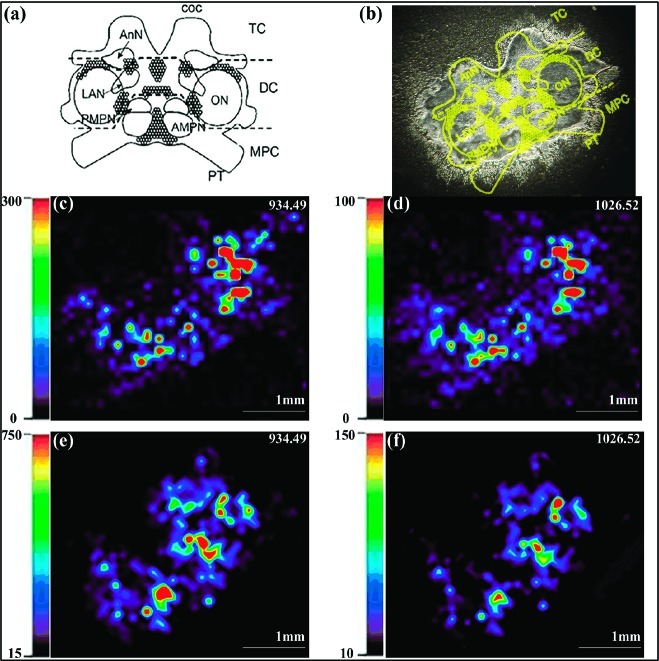
Figure 4.
Imaging mass spectrometry of C. sapidus brain shows the colocalization of CabTRP Ia and CalsTRP. (a) Representation of the ventral surface of the isolated brain with labeled neuropil region and neuron clusters. The main body of the decapod crustacean brain includes the median protocerebrum (MPC), deutocerebrum (DC), and tritocerebrum (TC). Each circumesophageal commissure (coc) projects from the tritocerebrum to the thoracic ganglion (TG), part way between which it contains the CoG (not shown). Five major brain neuropil regions include the anterior (AMPN) and posterior medial protocerebral neuropil (PMPN), olfactory lobe (ON), lateral antenna I neuropil (LAN), and antenna II neuropil (AnN). Note: not all neuropil regions are indicated. (b) An optical image of one slice of C. sapidus brain before application of MALDI matrix, with the brain regions highlighted. (c, d) MALDI-MS images of (c) CabTRP Ia and (d) CalsTRP showing their distribution in an unfed C. sapidus brain. (e, f) MALDI-MS images of (e) CabTRP Ia and (f) CalsTRP in a fed C. sapidus brain. The relative abundance is highlighted with a color-scale bar in each respective panel. Triplicate experiments were performed, and same results were obtained.