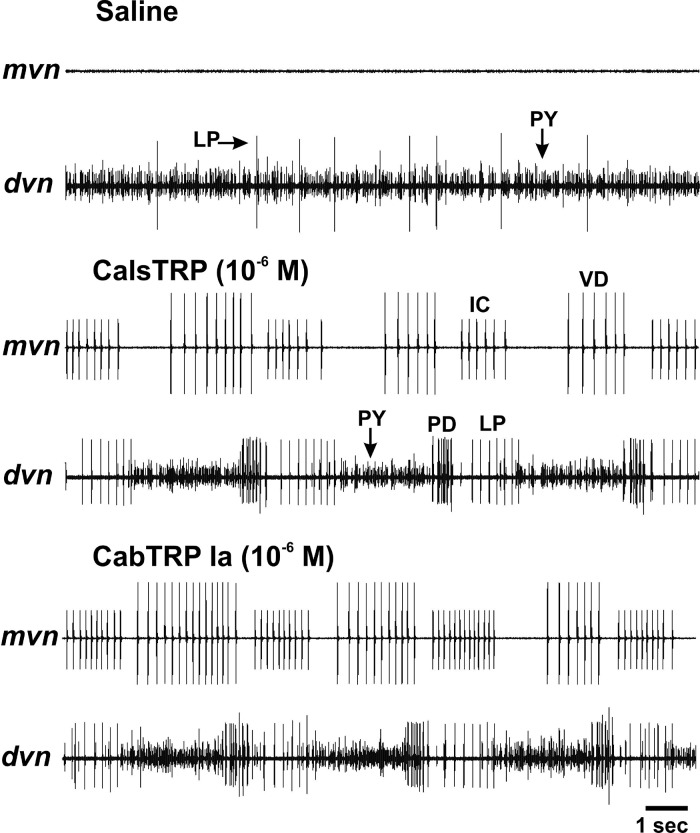
Figure 6.
Bath applied CalsTRP and CabTRP each activate the pyloric rhythm in the C. sapidus STG. Top: In this preparation, there was no ongoing pyloric rhythm during saline superfusion. As commonly occurs under this condition, there was regular spontaneous activity in the PY motor neurons and intermittent activity in the LP motor neuron (dvn). Middle: CalsTRP application activated the pyloric rhythm. Note the rhythmic, repeating coordinated bursting of the pyloric motor neurons in the dvn (LP, PY, PD) and mvn (IC, VD) nerves. As commonly occurs in other species, there was temporally overlapping activity between the LP and IC neurons and between the VD and PY neurons. Bottom: In the same preparation, CabTRP Ia application also activated the pyloric rhythm. Note the similarity of the rhythms in the presence of each peptide. There was a 1 h saline wash between the two peptide applications and after the second of the applications. Each pyloric rhythm terminated well before the end of the saline wash. The time scale bar pertains to all three panels.