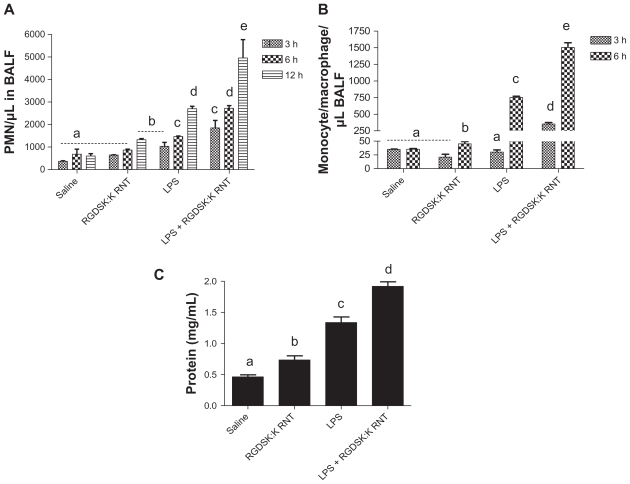
Figure 3.
Differential cell count and protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Total and differential cell count was performed in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid 3, 6, or 12 hours following treatment. Numbers of polymorphonuclear cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were significantly higher in the lipopolysaccharide and K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotube groups compared with saline controls. However, the lipopolysaccharide + K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotube treatment group showed robust polymorphonuclear emigration at all time points (A). Lipopolysaccharide resulted in an increase in emigration of monocytes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after 6 hours (B). Treatment with K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotubes had no effect on monocyte emigration compared with the saline control at all time points tested. Interestingly, mice treated with lipopolysaccharide and K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotubes showed a significant increase in monocyte emigration. Total protein analysis in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid showed a significant increase in protein content in the lipopolysaccharide and K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotube treatment groups (C). Interestingly, K90/RGDSK10 rosette nanotubes significantly proved the effect of lipopolysaccharide.
Note: Groups bearing different superscripts were significantly different (P < 0.05), while the groups with similar superscripts did not differ.