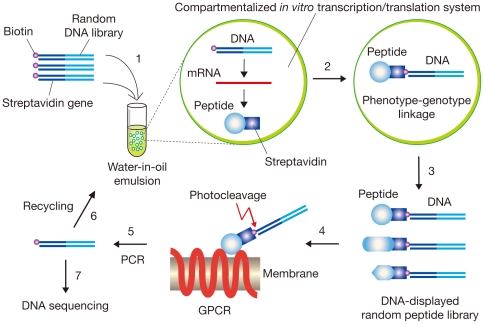
Figure 1. Schematic representation of DNA display selection of peptide ligands for GPCR expressed on cells.
A streptavidin gene-fused random DNA library labeled with biotin through a photocleavable linker is introduced into an in vitro transcription/translation system (Step 1). A single DNA molecule compartmentalized in a reversed micelle of water-in-oil emulsions is transcribed and translated in vitro (Step 2). In each compartment, a translated streptavidin-fused peptide (phenotype) binds to its encoding DNA (genotype) via the biotin label, and a mixture of DNA-peptide conjugates is recovered from the emulsions (Step 3). The resulting DNA-displayed random peptide library is affinity-selected with GPCR-expressing mammalian cells, and the DNA portion of binding molecules is eluted by photocleavage (Step 4). The selected DNA is amplified by PCR (Step 5) and used for the next round of enrichment (Step 6) or cloning and sequencing (Step 7).