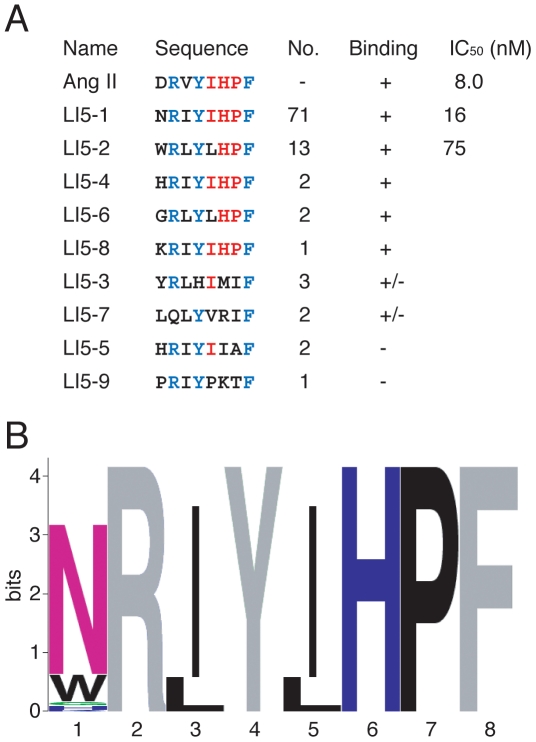
Figure 4. Amino acid sequences of selected clones from the randomized library-I.
(A) The designed sequence is XRΩYΩXΩF where X = F, L, I, M, V, S, P, T, A, Y, H, Q, N, K, D, E, C, W, R or G; and Ω = F, L, I, M, V, S, P, T or A. Fixed residues are shown in blue, and conserved residues are red. The number of clones containing each sequence is indicated. Sequences of seven clones with a frameshift in the preceding linker region are not shown. The binding activity (+, specific binding; +/−, nonspecific binding; −, no binding) of each peptide is also shown in Figures 6 and 7. IC50 was determined by means of competitive binding assays at various concentrations of synthetic peptides (see MATERIALS AND METHODS and Figure S1). (B) Sequence logos representation [45], [46] of the peptide sequences with specific binding activity (+). The height of each column reflects the bias from random of particular residues. Fixed residues are shown in gray. Polar amino acids containing an amide group (Q, N) and the rest of them are shown in purple and green, respectively, basic charged residues in deep blue, and hydrophobic residues in black.