Fig. 3.
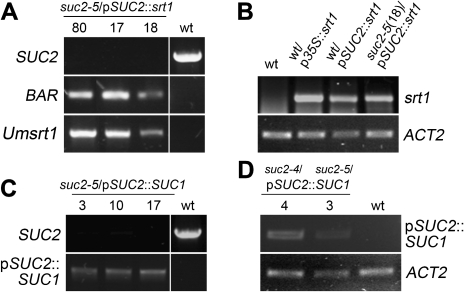
Genotyping of suc2/pSUC2::srt1 and suc2/pSUC2::SUC1 plants and determination of transcript abundance. (A) PCR analyses with genomic DNA from suc2/pSUC2::srt1 showing the absence of the SUC2 wt allele and the presence of the BAR gene and of srt1 in three different suc2/pSUC2::srt1 lines (#17, #18, #80). Control PCRs were performed on wt genomic DNA to visualize the SUC2 gene fragment, or on wt/pSUC2::srt1 genomic DNA to show the identity of the amplified BAR and Umsrt1 fragments. (B) Comparative RT-PCR analyses of srt1 transcript abundance on total RNA from wt, wt/p35S::srt1 and wt/pSUC2::srt1 source leaves or from entire suc2/pSUC2::srt1 plants showing srt1 transcripts only in transgenics. ACT2 levels are shown as controls. (C) PCR analyses on genomic DNA from three different suc2/pSUC2::SUC1 lines (#3, #10, #17) showing the absence of the SUC2 wt allele and the presence of the pSUC2::SUC1 insertion. Control PCRs on genomic DNA from wt plants identified the SUC2 gene and failed to amplify the mutant SUC1 allele. (D) RT-PCR analyses on total RNA from source leaves of two different suc2/pSUC2::SUC1 lines (#3, #4) and of wt plants identifying SUC1 mRNA transcribed from the pSUC2::SUC1 insertion only in transgenics. ACT2 transcript levels are shown as controls.