Figure 3.
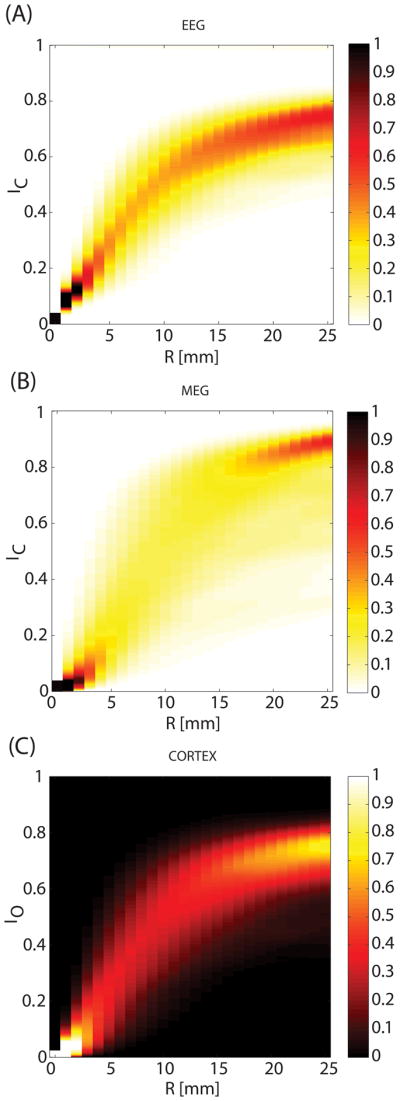
Dependence of the cancellation index IC upon patch radius R. The cancellation index IC measures the extent to which the signal generated by an activation patch is cancelled at the sensors. (A) The Probability Density Function (PDF) of the IC for EEG computed over all cortical dipoles as a function of R, normalized by the largest probability value (i.e. the mode of the distribution; in other words, PDF(IC)/max{PDF(IC)} is depicted). At R = 0 mm, the patch consists of one dipole and cancellation is minimal, implying that IC = 0. As patch radius increases from 0 to about 1 cm, the mode of the cancellation index distribution increases linearly (see text for details). (B) As in (A), for MEG. (C) As in (A), for the source disparity index IO.
