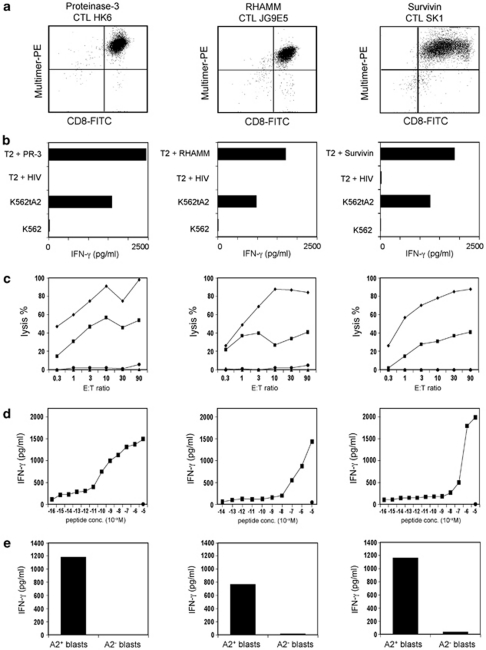
Figure 2.
CTL clones against PR-3, RHAMM, and Survivin, respectively, recognize the corresponding peptide epitopes. (a) FACS staining of the different CTL clones with the respective multimers. (b) The different CTL clones were co-cultivated with T2 cells loaded with PR-3169−177, RHAMM165−173, Survivin95−104 or HIVpol476−484, K562tA2, K562 or MCF7. The IFN-γ concentration of the supernatant was determined by ELISA. (c) Differential lytic activity of HLA-A2-restricted PR-3169−177-, RHAMM165−173- or Survivin95−104-directed CTL clones against T2 cells loaded with the respective peptide (⧫) and HLA-A2+ K562tA2 cells (▪). T2 cells loaded with the irrelevant peptide HIVpol476−484 (▴) and K562 cells (•) were used as negative ctrl. (d) Functional avidity of CTL clones was determined by the recognition of T2 cells pulsed with graded amounts of peptides. (e) The different CTL clones were co-cultivated with FLT3-ITD+ blasts of an HLA-A2+ AML patient or with blasts of an HLA-A2− AML patient. The IFN-γ concentration of the supernatant was determined by ELISA.