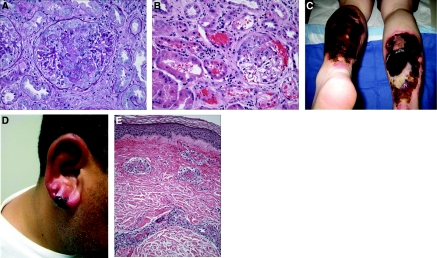
Figure 1.
(A) Kidney biopsy. The glomerulus reveals fibrinoid necrosis of the central part of the tuft associated with focal leukocytoclasia and a small cellular crescent filling the upper portion of Bowman's space; there is no significant hypercellularity of the uninvolved segments of the tuft. (Periodic acid-Schiff). (B) Kidney biopsy. The cortex shows an active glomerulitis with a small cellular crescent that has resulted in prominent bleeding into Bowman's space and the tubules. Mild interstitial inflammation is also present. (Hematoxylin & eosin). (C) Necrotic skin lesions. Large areas of full thickness, necrotic ulceration, near circumferential over both lower extremities. (D) Earlobe vasculitis. Purpuric violaceous lesion is seen with surrounding erythema. Biopsy revealed leukocytoclastic vasculitis. (E) Skin biopsy. The small vessel in the dermis shows active inflammation, with associated fibrinoid necrosis of the wall, leukocytoclasia, and thrombosis. The perivascular space reveals edema and extravasation of red blood cells. (Hematoxylin & eosin).