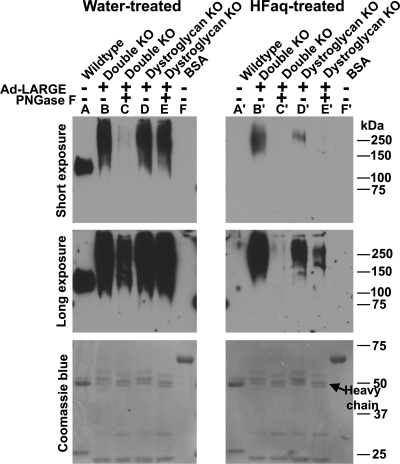
Fig. 5.
IIH6C4 immunoreactivity generated by overexpressing LARGE in POMT2/DG double-KO cells was sensitive to treatment with PNGase F and HFaq. POMT2/DG double-KO neural stem cells were infected with Ad-LARGE. VIA4-1 immunoprecipitate were isolated from the lysates and some were then treated with PNGase F. The samples were divided into equal halves and run in duplicate on SDS–PAGE. After transfer to the PVDF membrane, one set of the samples on PVDF membrane were treated with HFaq. Western blot analysis with IIH6C4 antibody was then carried out. Top panel, short exposure (45 s); middle panel, long exposure (5 min); bottom panel, Coomassie blue staining. (A and A′) Anti-β-DG immunoprecipitates from wild-type neural stem cells. IIH6C4 immunoreactivity on co-immunoprecipitated α-DG was completely abolished by HFaq treatment. (B and B′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from double-KO cells. HFaq treatment dramatically reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity. (C and C′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from double-KO cells treated with PNGase F. PNGase F treatment dramatically reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity (compare C with B). HFaq treatment further reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity (compare C′ with C). (D and D′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from DG KO neural stem cells. HFaq treatment dramatically reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity. (E and E′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from DG KO neural stem cells treated with PNGase F. PNGase F treatment reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity slightly (compare E with D). However, further HFaq treatment dramatically reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity (compare E′ with D′). (F and F′) BSA loading control. HFaq treatment did not change band intensities of BSA and other blotted proteins as revealed by Coomassie blue staining.