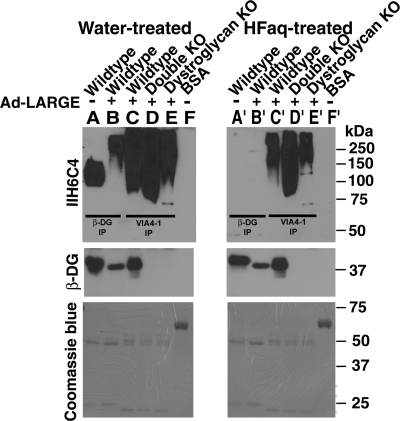
Fig. 7.
HFaq treatment completely removed IIH6C4 immunoreactivity on LARGE-hyperglycosylated α-DG. Anti-β-DG or VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates were isolated from the lysates of neural stem cells that were infected with Ad-LARGE and separated by SDS–PAGE. After transfer to the PVDF membrane, the samples were treated with water (A–F) or HFaq (A′–F′). Western blot analyses with IIH6C4 and anti-β-DG were then carried out. (A and A′) β-DG immunoprecipitates from wild-type neural stem cells. (B and B′) β-DG immunoprecipitates from LARGE-overexpressing wild-type neural stem cells. IIH6C4 immunoreactivity on co-immunoprecipitated α-DG was completely abolished by HFaq treatment regarding of the overexpression of LARGE. (C and C′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from LARGE-overexpressing wild-type neural stem cells. (D and D′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from double-KO cells with LARGE overexpression. (E and E′) VIA4-1 immunoprecipitates from DG KO neural stem cells with LARGE overexpression. HFaq treatment dramatically reduced IIH6C4 immunoreactivity but with some residue signals (compare lanes C–E with C′–E′). (F and F′) BSA loading control. In the western blotting with anti-β-DG, signals were detected from wild-type cells (lanes A–C and A′–C′) but not from KO cells (lanes D and E and D′ and E′). HFaq treatment did not change the immunoreactivity of β-DG (compare lanes A–C with A′–C′). HFaq treatment did not change the band intensities of BSA and other blotted proteins as revealed by Coomassie blue staining.