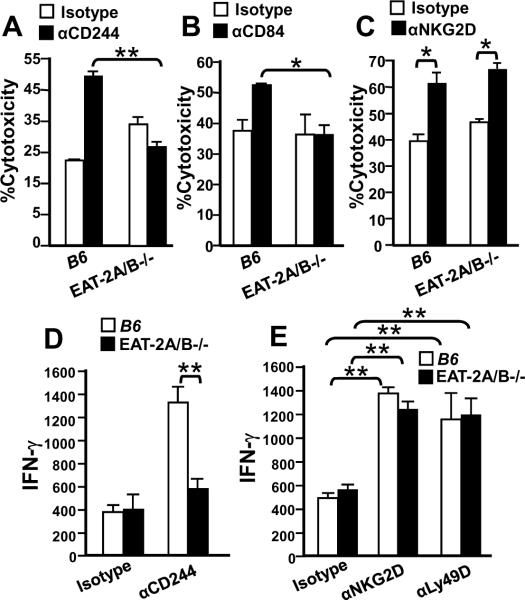
FIGURE 3. Defective αCD244 or αCD84 redirected killing and IFN-γ production by EAT-2A/B−/− NK cells.
NK cells from the spleens of wt or EAT-2A/B−/− mice were were cultured with IL-2-containing medium for seven days and analyzed in a redirected killing assay against the FcγR+ P815 target cells either in the absence or presence of anti-CD244 (A) anti-CD84 (B) or anti-NKG2D (C) mAbs. The lytic activity of wt or EAT-2A/B−/− NK cells was tested against P815 target cells by measuring 51Cr (A and C) or LDH (B) released into the cell supernatants. Wt or EAT-2-A/B−/− NK cells purified from the spleens were cultured in the presence of IL-2. At day 7, the NK cells were stimulated with anti-CD244 (5μg/ml) (D), anti-NKG2D (5μg/ml) or anti-Ly49D (5μg/ml) (E) mAbs for 24 hours. Culture supernatants were harvested and IFN-γ production was quantified by ELISA. Pooled data from three independent experiments were shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Error bars represent SD.