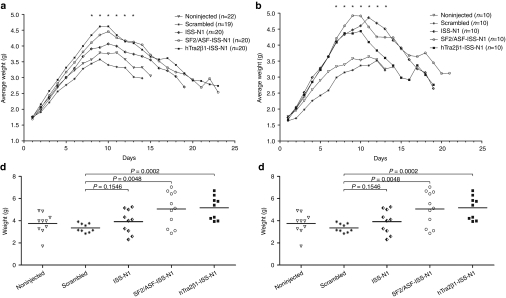
Figure 4.
Bifunctional RNAs injected animals were heavier than untreated spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) controls starting at PND6. Intracerebroventricular (ICV) injections of 2′-O-methyl intronic splicing silencer N1 (ISS-N1) bifunctional RNAs into SMNΔ7 mice on PND1, PND3 and PND5. (a) Total body weight was measured daily for noninjected, scrambled RNA, ISS-N1, SF2/ASF-ISS-N1, and hTra2β1-ISS-N1 injected mice with oligo concentration of 1 µg/µl. (b) Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) animals injected with the same bifunctional RNAs and controls with an oligo concentration of 10 µg/µl. Mice were weighed daily after injection. Days with significant weight gain are indicated with (*). (c) Individual weights on PND11 for all animals treated with 1 µg/µl of 2′-O-methyl ISS-N1 bifunctional RNAs. Student's t-test was used to compare each group against the scrambled control: ISS-N1 P = 0.0262; SF2/ASF P = 0.005; hTra2β1-ISS-N1 P = 0.0021. (d) Individual weights on PND11 for animals treated with 10 µg/µl of 2′-O-methyl ISS-N1 bifunctional RNAs. Student's t-test comparing each group against the scrambled control: ISS-N1 P = 0.1546; SF2/ASF P = 0.0048; hTra2β1-ISS-N1 P = 0.0002. SMN, survival motor neuron