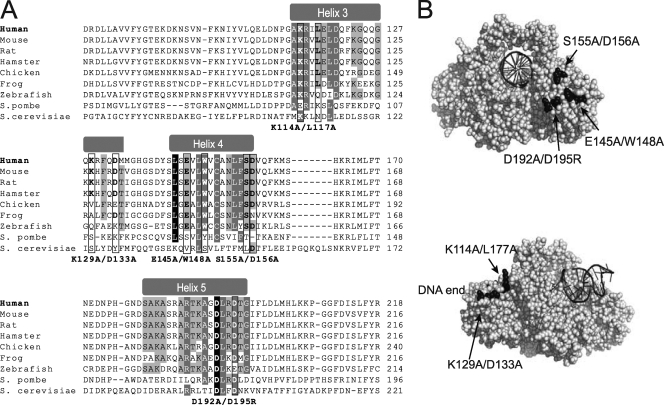
Fig 1.
(A) Sequence alignment of the Ku70 N-terminal vWA domain (α-helices 3 to 5) from a selection of Ku70 eukaryotic homologs. The position of the vWA domain α-helices is indicated at the top. Conservation between species of the residues within α-helices 3 to 5 is highlighted according to percent identity (PID) (light gray, >40%; dark gray, >60%; black, >80% PID). The residues mutated in this study are boxed, and the substitutions introduced are indicated below the alignments. (B) Space-filling representations of the human Ku dimer structure bound to DNA (72) (Protein Data Bank no. IJEY; depicted using PyMol). The upper image shows the front view of the Ku dimer (facing the DNA end). The Ku70 vWA domain E145/W148, S155/D156, and D192/D195 residues are highlighted in black, and their position is indicated. DNA is represented as a black helix. The lower image shows the side view of the Ku dimer (DNA end to the left). The position of the Ku70 vWa domain K114/L117 and K129/D133 residues is shown.