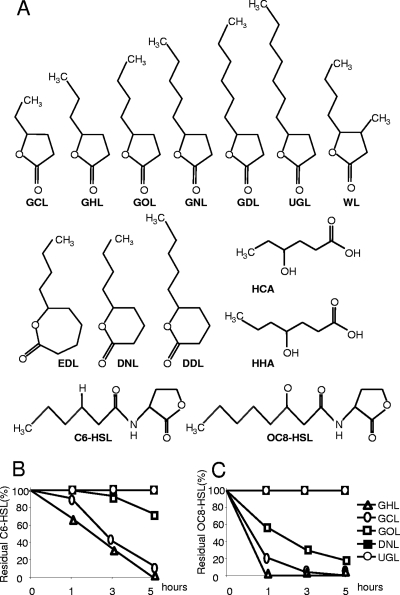
Fig 1.
Lactones and derivatives used in this study and kinetics of AHL inactivation by bacterial consortia stimulated by lactones. (A) Structural formulae of γ-caprolactone (GCL), γ-heptalactone (GHL), γ-octalactone (GOL), γ-nonalactone (GNL), γ-decalactone (GDL), undecanoic γ-lactone (UGL), Whiskey lactone (WL), ε-decalactone (EDL), δ-nonalactone (DNL), δ-decalactone (DDL), 4-hydroxyhexanoic acid (HCA), 4-hydroxyheptanoic acid (HHA) (the latter two compounds result from lactonolysis of GCL and GHL, respectively), N-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone (C6-HSL), and N-3-oxo-octanoyl-homoserine lactone (OC8-HSL). The bacterial consortia, obtained after enrichment on the indicated compounds or mannitol as a sole carbon source, were tested for their capacity to inactivate C6-HSL (B) and OC8-HSL (C). At each time point, residual AHL was measured and expressed as a percentage of residual AHL in the reference assay with the mannitol-only consortium. Kinetics obtained with DNL and UGL are superimposed.