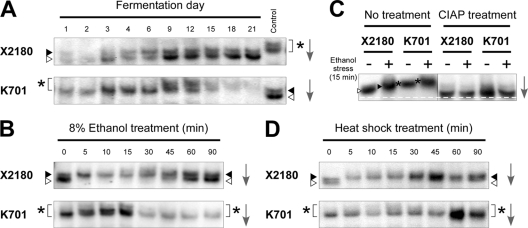
Fig 2.
Immunoblot analyses of Hsf1p in laboratory and sake yeast strains. (A) Phosphorylation states of Hsf1p in X2180 (upper) and K701 (lower) during sake fermentation. The rightmost lanes show the same samples as day 9 of K701 (upper) and day 21 of X2180 (lower) as controls. (B) Phosphorylation states of Hsf1p under 8% ethanol stress in X2180 (upper) and K701 (lower). (C) Effects of phosphatase treatment on Hsf1p. The cell extracts of X2180 and K701 under nonstress and 8% ethanol stress conditions were incubated in the absence (left panel) or presence (right panel) of calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) and subjected to immunoblot analysis. The white dashed line represents the position of furthest migration of the dephosphorylated forms of Hsf1p. (D) Phosphorylation states of Hsf1p under heat shock (41°C) in X2180 (upper) and K701 (lower). White triangles, gray triangles, and asterisks indicate hypophosphorylated, hyperphosphorylated, and superhyperphosphorylated forms of Hsf1p, respectively, whose positions were determined by comparison with the control samples analyzed in the same gel. The arrows indicate the direction of electrophoretic migration.