Fig 1.
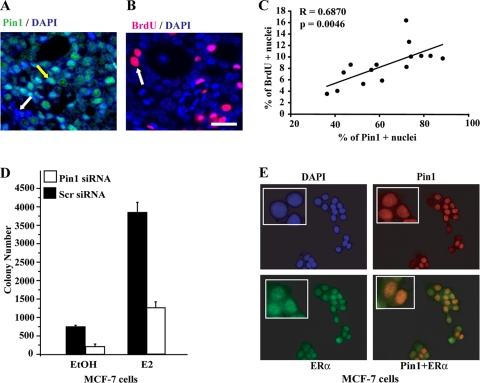
Pin1 is important for growth of ERα-positive breast cancer cells. (A and B) Immunohistochemistry of Pin1 and BrdU in mammary tumors in carcinogen-treated ovariectomized rats implanted with pellets releasing E2. Shown are representative images of Pin1 (green), BrdU (magenta), and nuclear diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Merged images show nuclear Pin1 (teal) with a nuclear Pin1-positive cell pointed out with a yellow arrow and a Pin1− cell indicated with a white arrow (A). A BrdU+ proliferating cell is indicated with a white arrow (B). Bar, 50 μm. (C) Pin1 expression correlates with proliferation. Individual mammary tumors (n = 15) are represented by a single dot. The numbers of Pin1+ or BrdU+ cells detected by immunofluorescent labeling were quantified from captured images, and the numbers of positive cells are expressed as the percentage of total tumor cells counted. Results are means ± SEM. Correlation coefficient R = 0.6871 (P < 0.005). (D) Pin1 is essential for growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. MCF-7 cells were transfected with Pin1 siRNA or control scrambled (Scr) siRNA and treated with EtOH or 10 nM E2. Growth was assessed by soft agar colony formation assay after 14 to 16 days of treatment. The number of colonies was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Data are means ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. (E) Immunocytochemistry of Pin1 and ERα in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. MCF-7 cells were stained for nuclear DAPI (blue), Pin1 (red), and ERα (green). The insets shows positive cells in a magnified image. A merged image of Pin1 and ERα is shown in yellow.