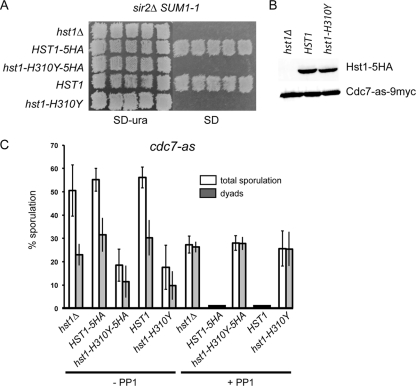
Fig 3.
Phenotypic analysis of an hst1 catalytic mutant in suppressing SUM1-1 in vegetative cells and the meiotic arrest conferred by cdc7-as plus PP1. (A) A MATα sir2Δ SUM1-1 hst1Δ LYS1 haploid strain (YHR38) was transformed with pRS306, HST1-5HA, hst1-H310Y-5HA, HST1, or hst1-H310Y. Different transformants were patched onto SD-Ura plates and then replica plated to a lawn of MATa lys1 cells. Diploids were selected on SD plates to test for mating. (B) Total extracts from log-phase cells of a cdc7-as hst1Δ (NH1061) diploid transformed with either pRS306, HST1-5HA (pHL16), or hst1-H310Y-5HA (pHL16-H310Y) were probed with anti-HA antibodies. As a loading control, anti-Myc antibodies detected Cdc7-as-9myc. (C) cdc7-as hst1Δ, cdc7-as HST1-5HA, cdc7-as hst1-H310Y-5HA, cdc7-as HST1 (pHL17), and cdc7-as hst1-H310Y (pHL17-H301Y) cells were subjected to the “quick sporulation” protocol in the absence or presence of 15 μM PP1, and ascus formation was monitored using phase-contrast microscopy. Two hundred cells were counted for each culture for each strain, and at least three independent colonies were monitored for each strain. Error bars indicate the standard deviations.