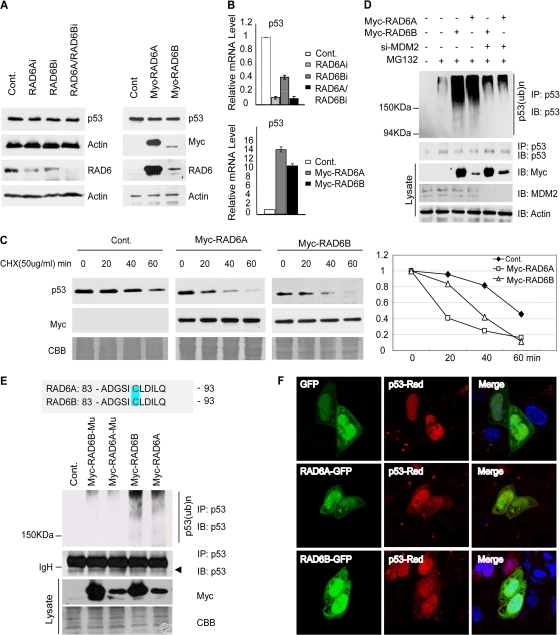
Fig 1.
RAD6 regulates p53 degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. (A) Neither the depletion nor the overexpression of RAD6 has an obvious effect on p53 protein levels. HL-7702 cells (left) or HeLa cells (right) were transfected with RAD6 siRNAs or Myc-RAD6 constructs as indicated. The immunoblot was stained with anti-p53 or anti-Myc antibodies plus antiactin antibodies as a loading control. (B) Depletion or overexpression of RAD6 affects the p53 mRNA level. HL-7702 cells were treated with nonspecific control (Cont.) or RAD6 siRNAs (RAD6Ai or RAD6Bi) (top). HL-7702 cells transfected with Myc control, Myc-RAD6A, or Myc-RAD6B plasmids are indicated on the bottom. Total RNA was prepared and subjected to real-time RT-PCR analysis using specific primers for p53 and GAPDH (as a control). (C) Overexpression of RAD6 decreases the half-life of p53 in HL-7702 cells. HL-7702 cells were transfected with or without Myc-RAD6 and subsequently treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated periods of time. Immunoblots were stained with antibodies against p53 or the Myc tag (to visualize Myc-RAD6). Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining is shown as an internal control. (D) RAD6 overexpression promotes p53 ubiquitination in an MDM2-dependent manner. HL-7702 cells were transfected with (+) or without (−) Myc-RAD6 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of MDM2 siRNA and treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (−) or MG132. An anti-p53 antibody was used to visualize the amount of precipitated p53 and ubiquitinated p53. The expression of Myc-RAD6 (Myc) and MDM2 is shown in the lower panels. (E) RAD6 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymatic activity is required for its ubiquitination of p53. HL-7702 cells were transfected with or without (Cont.) Myc-RAD6 constructs (Myc-RAD6A or Myc-RAD6B) or their Myc-RAD6-C88A mutants (Myc-6A-C88A or Myc-6B-C88A) and treated with DMSO (Cont.) or MG132. Anti-p53 and antiubiquitin antibodies were used to visualize the amounts of precipitated p53 and ubiquitinated p53. The expression of Myc-RAD6 mutants (Myc) is shown in the lower panels. (F) RAD6 overexpression promotes the cytoplasmic localization of p53. H1299 cells transfected with green fluorescent protein (GFP) or RAD6-GFP together with the p53-DsRed2 construct were subjected to an immunofluorescence assay.