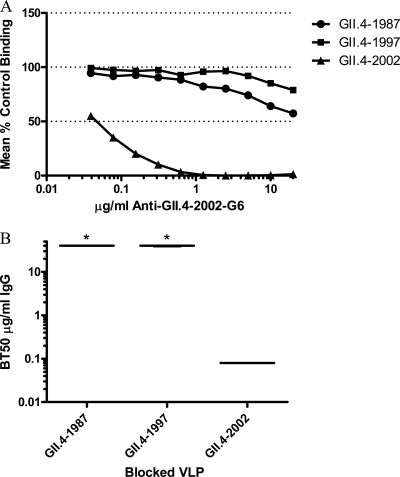
Fig 5.
Blockade of GII.4 VLP-PGM interactions by GII.4-2002-G6. Increasing concentrations of anti-GII.4-2002-G6 were incubated with GII.4 VLPs positive for EIA reactivity, and the mean percent control binding was calculated by comparing the amount of VLP bound to PGM in the presence of antibody pretreatment to the amount of VLP bound in the absence of antibody pretreatment. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means. (B) The Mean MAb concentration (μg/ml) needed to block 50% of GII.4 VLP ligand binding is indicated by the line in the graph. The upper and lower broken lines in the graph represent the maximum and minimum values. Asterisks indicate VLPs with BT50s significantly different from that of GII.4-2002.