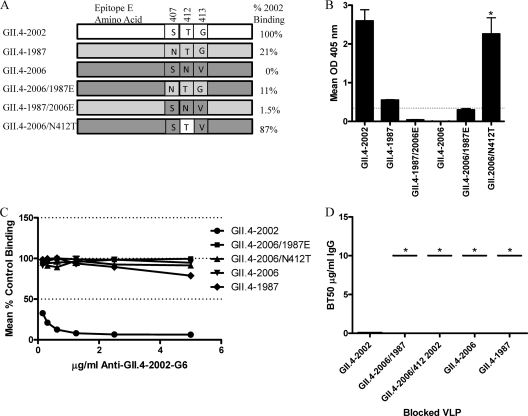
Fig 8.
Characterization of epitope E, a GII.4-2002-specific potential neutralization epitope. (A) VLPs engineered to contain variations of epitope E were assembled to test the impact of the epitope and the nonepitope backbone on anti-GII.4-2002-G6 binding and neutralization. (B) Anti-GII.4-2002-G6 EIA reactivity to epitope E constructs. Asterisks indicate chimeric VLPs with reactivity significantly different from that of the parental VLPs. (C) Blockade of epitope E constructs binding to PGM by anti-GII.4-2002-G6. (D) The mean MAb concentration (μg/ml) needed to block 50% of GII.4 VLP ligand binding is indicated by the line in the graph. The upper and lower broken lines in the graph represent the maximum and minimum values. Asterisks indicate VLPs with BT50s significantly different from that of GII.4-2002.