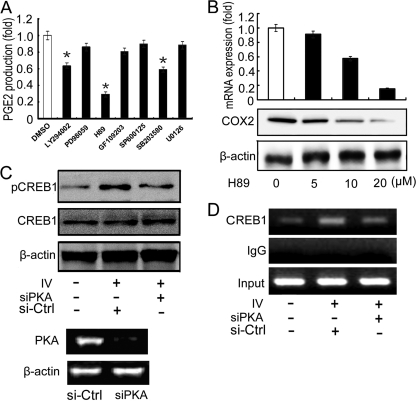
Fig 7.
The PKA-CREB pathway is involved in IV-induced COX2 expression. (A) A549 cells were infected with IV (MOI = 1) and treated with seven different signaling pathway inhibitors. After incubating for 24 h, cells were harvested and PGE2 was measured. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) served as the negative control. Data shown are mean ± SE; n = 3 (*, P < 0.05). (B) A549 cells were treated with the PKA inhibitor H89 at various doses (0, 5, 10, and 20 μM). After 24 h of incubation, cells were harvested and COX2 expression was measured by real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting. DMSO served as the negative control. (C and D) Specific siRNA against PKA was transfected into A549 cells for 24 h. Cells were then infected with IV (MOI = 1) and harvested 24 h after infection, and Western blotting was performed with antibody specific for CREB1 or phospho-CREB1 (C), or cells were harvested for the detection of CREB1 binding activity by ChIP assay (D). Irrelevant siRNA served as the negative control. The efficiency of PKA-specific siRNA (siPKA) was tested by RT-PCR (C, bottom).