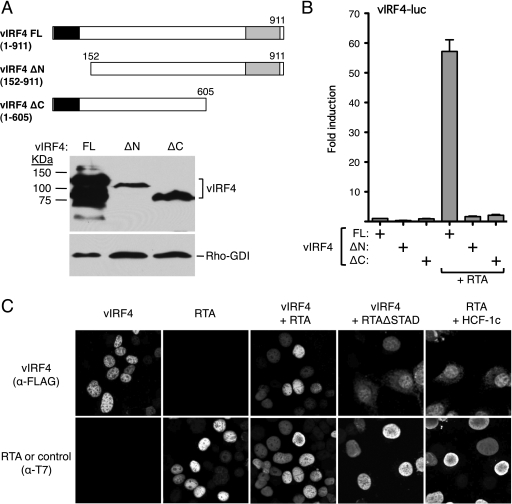
Fig 5.
N- and C-terminal domains of vIRF4 are required for RTA synergy. (A) Schematic showing limits of the N- and C-terminal vIRF4 truncations. Expression levels were assessed by immunoblotting using anti-vIRF4 antiserum (kind gift of Jae Jung and Hye-Ra Lee). (B) Activity assay in HeLa cells transfected with vIRF4-luc reporter (250 ng) and expression plasmids carrying full-length or truncated vIRF4 (200 ng) in the presence or absence of RTA (37.5 ng). Activity (fold induction) was calculated relative to that of the reporter with full-length vIRF4 only. Values represent the means and standard errors of the means of three independent transfections. (C) vIRF4 and RTA independently localize to the nucleus. Indirect immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells transfected with plasmids expressing T7-epitope-tagged RTA and Flag-epitope-tagged vIRF4 proteins (200 ng each). After fixation, coverslips were probed with a mix of anti-T7 (rabbit polyclonal) and anti-Flag (mouse monoclonal) antibodies followed by a mixture of anti-mouse and anti-rabbit fluorescence-coupled secondary antibodies.