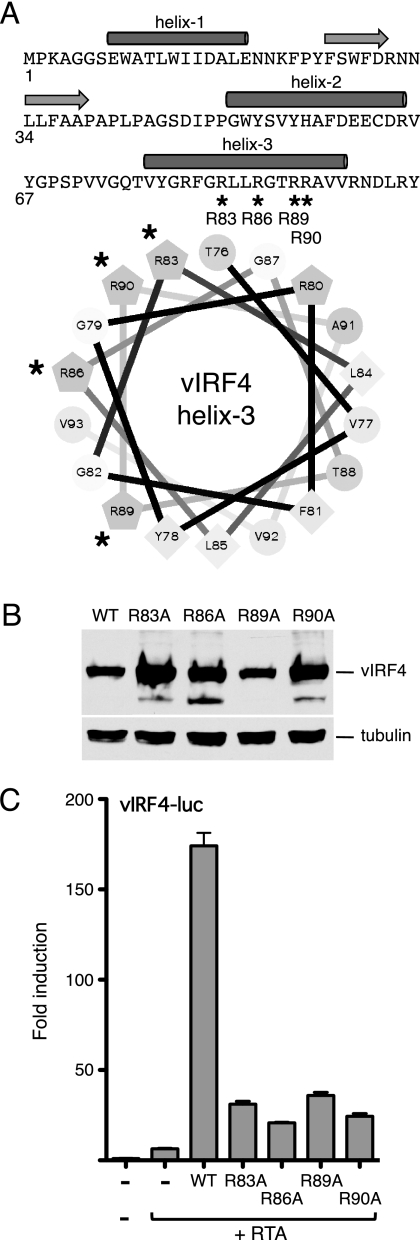
Fig 6.
Mutations in helix 3 of vIRF4 disrupt synergy with RTA. (A) Primary sequence of the vIRF4 N terminus (residues 1 to 98), showing the locations of the predicted α-helices (filled cylinders) and β-strands (horizontal arrows). Helix 3 is also shown as a helical wheel projection with hydrophobic residues (F, L, V, and Y) clustered on one face (lower right). The four arginine residues (R83, R86, R89, and R90) that were changed in turn to alanine are indicated with an asterisk. (B) Immunoblot (with anti-Flag antibody) of lysates prepared from cells transfected with each vIRF4 plasmid. The species corresponding to full-length vIRF4 is indicated. Equal loading was demonstrated by blotting for α-tubulin. (C) Activity assay using HeLa cells transfected with vIRF-luc (250 ng) and each vIRF4 derivative (200 ng) in the presence of RTA (37.5 ng). Fold induction was calculated relative to the reporter alone. Values represent the means and standard errors of the means of three independent transfections.