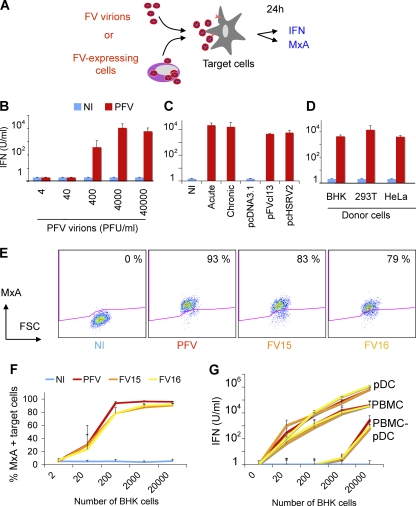
Fig 2.
Sensing of FV particles and FV-infected cells by hematopoietic cells. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental procedure. Target PBMCs were exposed to FV particles or cocultivated with FV-infected cells. After 24 h, type I IFN production was measured in supernatants, and expression of the IFN-stimulated gene MxA was monitored by flow cytometry. (B) IFN release by PBMCs exposed to FV particles. Whole PBMCs were exposed to the indicated doses (in PFU/ml) of PFV virions, obtained by ultracentrifugation of lysates from PFV-infected (PFV) BHK21 cells. Similar amounts of lysates from NI cells were used as a control. Type I IFN was measured after 24 h. Means ± the SD of at least three independent experiments are shown. (C) PBMCs recognize BHK21 cells infected with FV or transfected with PFV proviruses. Different types of FV-expressing BHK21 cells were used as donors. Acutely infected BHK21 cells (acute) correspond to cells used 3 to 5 days postinfection with FV. “Chronically” infected BHK21 cells (chronic) are maintained in long-term cultures by the addition of fresh BHK21 cells twice a week. BHK21 cells were also transfected with two reference PFV proviruses (pFVcl13 and pcHSRV2) or with a control plasmid (pcDNA3.1). These different donor cells were cocultivated with PBMCs and type I IFN was measured after 24 h. Means ± the SD of at least three independent experiments are shown. (D) IFN release by PBMCs exposed to various FV-expressing donor cells. PBMCs were also cocultivated with BHK21, 293T, or HeLa cells that had been transfected with PFV-encoding (pFVcl13) and control plasmid (pcDNA3.1). Type I IFN production was measured in the supernatants. Means ± the SD of three to five independent experiments are shown. (E) MxA expression in PBMCs. PBMCs were (i) cocultivated with noninfected BHK21 cells or with cells infected with PFV, FV15, or FV16, (ii) stained for MxA, and (iii) analyzed by flow cytometry. A representative experiment is shown. The percentage of MxA+ cells is indicated. (F) Dose-response analysis of MxA expression in PBMCs. PBMCs (1.25 × 105/well) were cocultivated with the indicated number BHK21cells infected with PFV, FV15, or FV16 (60 to 90% of the BHK21 cells were FV positive at the beginning of the coculture). Means ± the SD of MxA expression of three to five independent experiments are shown. (G) pDCs are the main hematopoietic cells producing type I IFN. Whole PBMCs, PBMCs depleted of pDCs (PBMC-pDCs; 1.25 × 105/well), or purified pDCs (0.25 × 105/well) were cocultivated with the indicated numbers of BHK21cells infected with PFV, FV15, or FV16. Type I IFN production was measured in the supernatants. Means ± the SD of three independent experiments are shown.