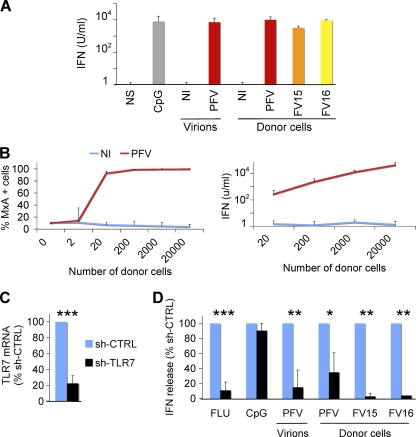
Fig 4.
FV Sensing by the Gen2.2 pDC cell line. (A) Type I IFN release by Gen2.2 cells in contact with FV particles or FV-infected cells. Gen2.2 cells (1.25 × 105/well) were either (i) not stimulated (NS), (ii) incubated with CpG (2 μM), lysates from noninfected (NI), or FV-infected (PFV) cells (4,000 PFU/ml), or (iii) cultivated with BHK21 cells (2 × 103/well) either not infected (NI) or infected with PFV, FV15, or FV16. Type I IFN production in supernatants was measured after 24 h. Means ± the SD of IFN release of four independent experiments are shown. (B) Dose-response analysis of type I IFN production. Gen2.2 cells were cocultivated for 24 h with the indicated number of BHK21cells and stained for MxA (left panel). The type I IFN production in supernatants was measured in supernatants (right panel). Means ± the SD of two (left panel) and four (right panel) independent experiments are shown. (C and D) Role of TLR7 in FV sensing. (C) Silencing of TLR7. Gen2.2 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing shRNAs against TLR7 (shTLR7) or an irrelevant target (shCTRL). The levels of TLR7 mRNA in transduced cells were measured by RT-PCR. The data are normalized to GAPDH mRNA and expressed as relative levels of mRNA compared to shCTRL cells. (D) Type I production in control and TLR7-silenced Gen2.2 cells. shCTRL and shTLR7 Gen2.2 cells were exposed for 24 h to FLUAV, CpG (2μM), PFV particles, or cocultivated with PFV-, FV15-, or FV16-infected BHK21cells (2 × 103/well). The type I IFN levels are expressed as the percentage of the signal obtained with shCTRL Gen2.2 cells. Means ± the SD of two to three independent experiments are shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.001.