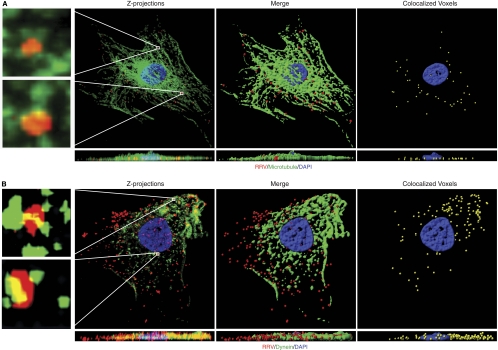
Fig 4.
Colocalization of RRV particles with microtubules and the dynein motor proteins. (A) Colocalization of RRV particles with microtubules. RFs infected with RRV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 50 were fixed at 1 h postinfection (hpi) and stained for RRV particles (red), microtubule cytoskeletons (green), and nuclei (blue). Z-stack images were acquired by Olympus FV1000 scanning confocal microscopy. Both the Z-projection and the XZ section showed colocalization of RRV particles with microtubules (yellow; left panel). Regions delineated by rectangle inserts were shown at higher magnifications in adjacent panels. 3D contoured images (middle and right panels) were generated with AutoQuant deconvolution (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Bethesda, MD) software and Imaris 3D image analysis software (Bitplane, Zurich, Switzerland). Corresponding XZ sections were visualized by rotating on the x axis to observe the location of virus particles. Movie S1 in the supplemental material corresponds to Fig. 4A. (B) Colocalization of RRV particles with dynein. RFs were infected with RRV for 1 h and stained for RRV particles and dynein heavy chain. Images were processed for 3D colocalization analysis. Regions delineated by rectangles are shown at higher magnifications in adjacent panels. Movie S2 in the supplemental material corresponds to Fig. 4B.