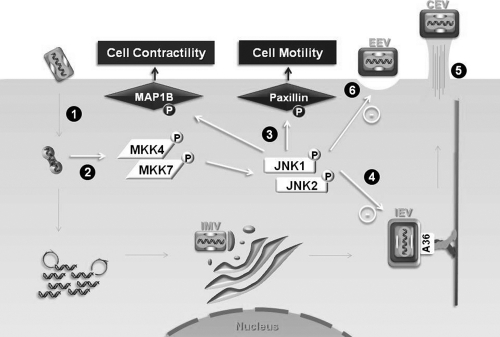
Fig 8.
Schematic representation of the VACV-stimulated MKK4/7-JNK1/2 pathway and its biological consequences. Soon after IMV penetration and uncoating (step 1), replication-competent virus is required for the stimulation of the MKK4/7-JNK1/2 pathway (step 2). The pathway does play a relevant role in virus-stimulated cell migration and cell contractility/morphology (step 3), although it does not affect viral productivity. IEV is then formed and transported to the cell periphery (step 4). Altered microtubule and actin cytoskeleton organization in the JNK-KO cells is followed by deregulated accumulation/release of viral enveloped form, i.e., increased accumulation of CEV (step 5) at the surface as well as release of EEVs (step 6).