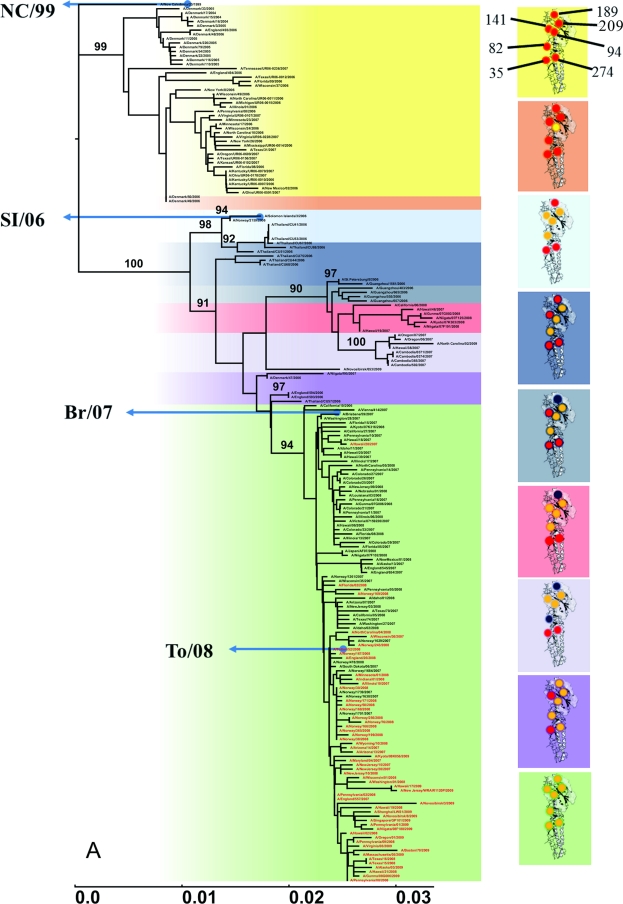
Fig 1.
Phylogenetic analyses of HA and NA of seasonal H1N1 viruses by using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replications. Oseltamivir-resistant isolates carrying NA 274Y are shown in red. (A) HA phylogenetic tree of selected seasonal H1N1 isolates from 2004 to 2009 (excluding 2009 pandemic H1N1 viruses). Branches are colored to reflect amino acid changes. Only bootstrap values of >90% are shown for each corresponding group. The scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The following vaccine strains are included in the tree as a reference: 2004-2007 season (NC/99), 2007-2008 season (SI/06), and 2008-2010 season (Br/07) vaccines. The To/08 virus used in this study is included in the oseltamivir-resistant 2007-2008 isolates (green box). The seven amino acid substitutions that occurred in the HA head and were maintained in subsequent viruses during HA evolution between 2004 and 2008 include D35N, T82K, Y94H, K141E, R189K, R209K, and E274K. HA amino acids of 2004-2005 isolates are represented by red spheres and changed to other amino acids (shown in yellow) in subsequent viruses. Occasional amino acid substitutions that are not listed in Table 1 appeared temporarily at two of these positions (blue spheres). (B) NA phylogenetic tree of prepandemic seasonal H1N1 strains from 2004 to 2009. To/08 NA is included in the oseltamivir-resistant 2007-2008 isolates.