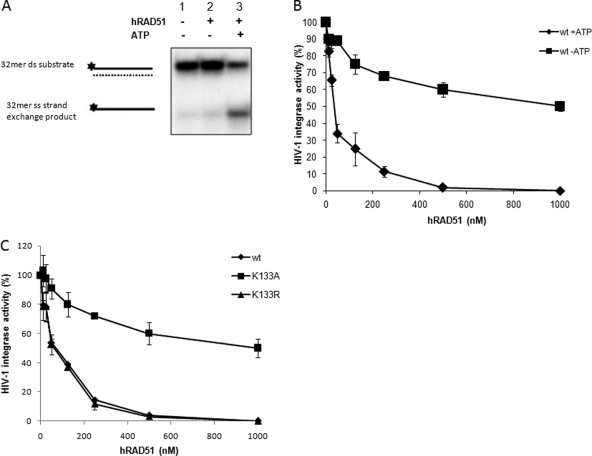
Fig 3.
Involvement of hRAD51 nucleofilament in inhibition of integration in vitro. (A) ATP-dependent strand exchange activity. The hRAD51 strand transfer reaction (left panel) was performed in the presence of 500 nM hRAD51 and in the absence or presence of 100 μM ATP. Products were loaded on nondenaturating 12% polyacrylamide gel. The single-stranded (ss) strand exchange product is shown, as well as the double-stranded (ds) 32-mer substrate. (B) ATP-dependent HIV-1 IN inhibition by hRAD51. Concerted integration reactions were performed under standard conditions with increasing concentrations of wild-type hRAD51 in the absence or presence of 100 μM ATP. Integration products were quantified on agarose gel. Values are percentages of donor DNA integrated as circular HSI and FSI plus linear FSI forms. (C) Inhibitory effect of hRAD51 mutants defective for DNA binding and/or nucleofilament formation on HIV-1 IN inhibition. Concerted integration reactions were performed under standard conditions in the presence of increasing concentrations of wild-type protein or K133R and K133A RAD51 mutants and 100 μM ATP. The reaction products were loaded on 1% agarose gel. Integration products were quantified on agarose gel. Values are percentages of donor DNA integrated as circular HSI and FSI plus linear FSI forms. The data reported are the means from at least three independent experiments ± standard deviations (error bars).