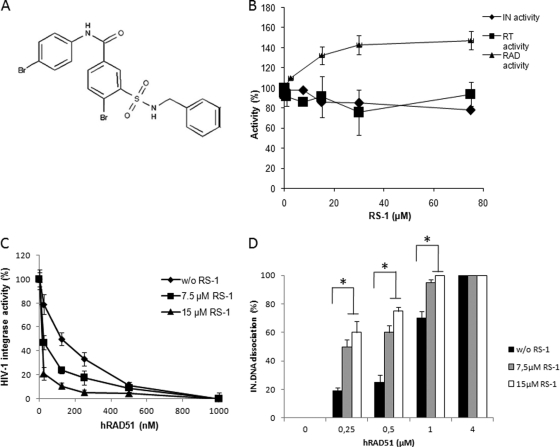
Fig 6.
In vitro effect of hRAD51 activity stimulation by RS-1 on its integration inhibition property. (A) Chemical structure of RS-1 {3-[(benzylamino)sulfonyl]-4-bromo-N-(4-bromophenyl)benzamide} molecule. (B) In vitro effect of RS-1 on HIV-1 IN, reverse transcriptase, and hRAD51 enzymes. The effect of RS-1 on in vitro integration was analyzed by using the concerted integration system with 600 nM IN, 150 ng of acceptor plasmid, and 15 ng of donor DNA. The effect of RS-1 on the RT enzyme was analyzed in a typical RNase H assay. The RS-1 effect on hRAD51 was measured in the strand exchange reaction shown in Fig. 2B in the presence of 500 nM hRAD51. The data reported are the means from at least two representative independent experiments ± standard deviations (error bars). One hundred percent corresponds to the activity observed in the absence of RS-1. (C) Effect of RS-1 on in vitro inhibition of HIV-1 IN activity by hRAD51. Increasing concentrations of wt hRAD51 were added in a standard concerted integration assay in the presence of 100 μM ATP and in the absence or presence of 7.5 or 15 μM RS-1. The data reported are the means from at least three independent experiments ± standard deviations (error bars). Integration is shown as the percentage of donor DNA integrated as circular HSI and FSI plus linear FSI forms. (D) Effect of RS-1 on hRAD51-mediated dissociation of the IN-DNA complex. The dissociation experiment was performed as shown in Fig. 4 with increasing concentrations of hRAD51 in the presence of 100 μM ATP and with or without 7.5 or 15 μM RS-1. The data reported are the means from at least three independent experiments ± standard deviations (error bars). A Student test was performed on serial values. *, P < 0.05.