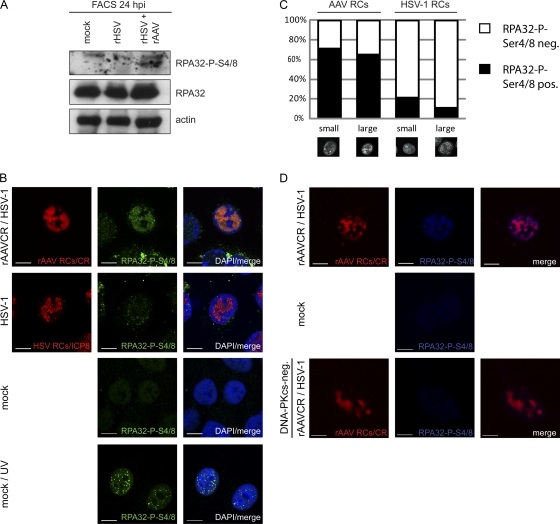
Fig 6.
Phosphorylation of RPA32 upon AAV2 and HSV-1 replication. (A) WB analysis of sorted AT22 IJE-T cells at 24 hpi. Cells were mock infected, infected with rHSV-1vECFP-ICP4 (rHSV; MOI, 4), or coinfected (rHSV + rAAV) with rHSV-1vECFP-ICP4 (MOI, 4) and rAAV2CR (MOI, 4,000). Sorted cells were subjected to WB analysis and analyzed with the antibodies indicated. (B) IF analysis of U2OS cells after infection with HSV-1 (MOI, 1.5) or rAAVCR (MOI, 250) and HSV-1 (MOI, 1.5) or mock infection at 24 h. UV-treated cells (10 J/m2) served as a positive control. rAAVCR and HSV-1 RCs (red) were visualized as described in the legend to Fig. 2. To detect phosphorylated RPA32, cells were stained with an antibody specific for RPA32-P-S4/8 and an FITC-labeled secondary antibody (green). Cellular DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of RPA32-P-S4/8 colocalization with small and large AAV2 or HSV-1 RCs in U2OS cells. Fifty cells per sample were counted. Black columns, RPA32-P-S4/8-positive viral RCs; open columns, RPA32-P-S4/8 negative viral RCs. (D) IF analysis of MO59J Fus1 or Fus9 (DNA-PKcs-negative) cells at 24 h after mock infection or coinfection with HSV-1 (MOI, 1.5) and rAAVCR (MOI, 250). rAAVCR RCs (red) were visualized as described in the legend to Fig. 2. Cells were stained with an antibody specific for RPA32-P-S4/8 and an AF405-labeled secondary antibody (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm.