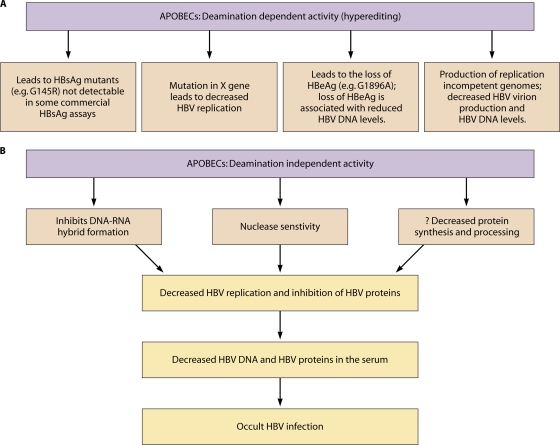
Fig 3.
Role of APOBEC deaminases in occult HBV infection. (A) Deamination activity of APOBEC protein converts cytosine to uracil in the HBV genome, leading to various mutations associated with occult HBV infection. (B) Deamination-independent activity of APOBEC deaminases inhibits DNA-RNA hybrid formation, increases susceptibility to nuclease digestion, and decreases protein processing, eventually leading to occult HBV.