Fig 6.
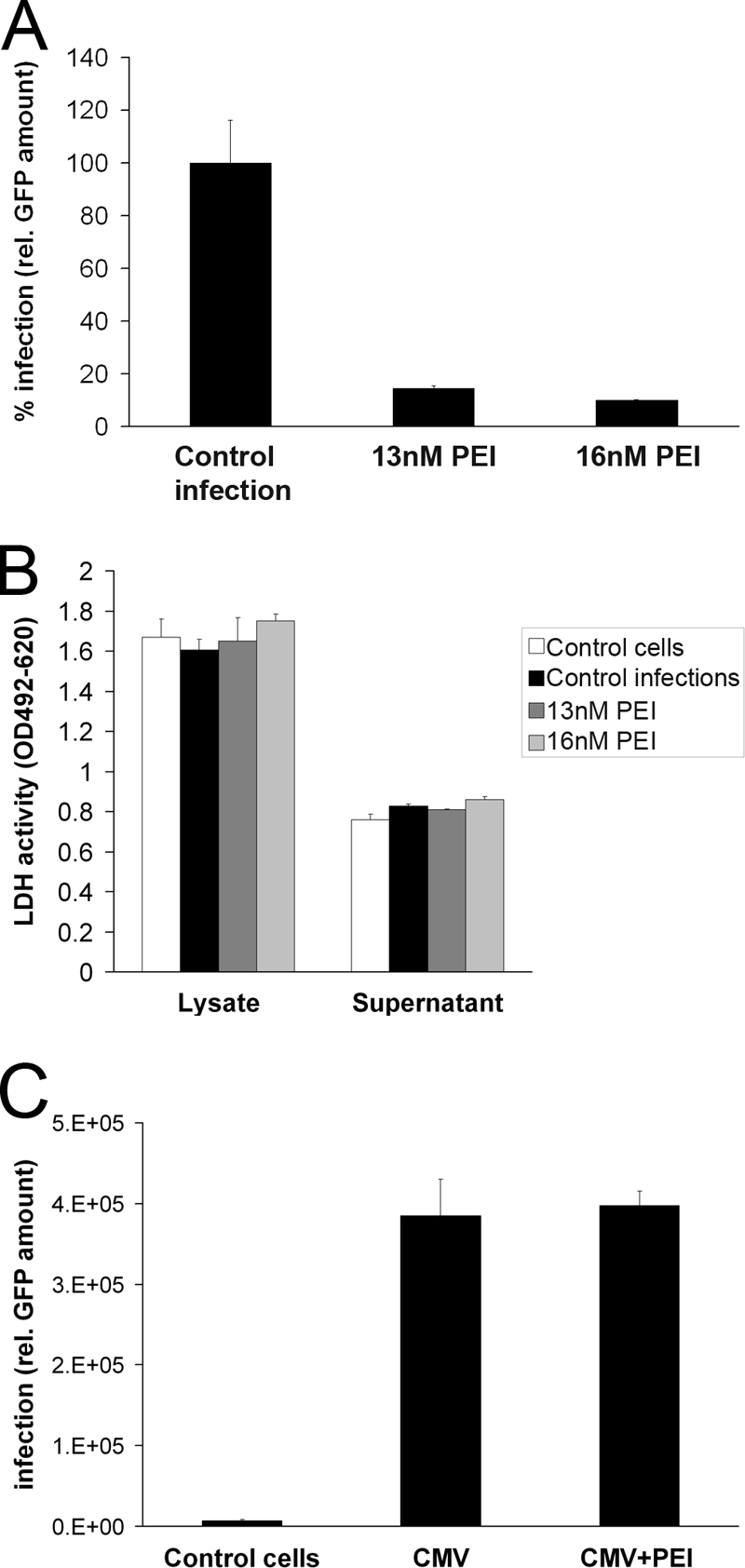
Impact of PEI on infection and spread of HCMV in permissive HFFs. (A) Inhibition of HCMV dissemination in HFF cultures by PEI. Cells were infected with RV-ΔUS2-11_GFP (MOI, 0.003). At 10 h p.i., 13 or 16 nM PEI was added to the culture medium. Additional PEI was supplemented in 24-h intervals. Total viral load was quantified 10 days after infection by measuring GFP. Bars represent the mean of three individual experiments ± SD. Control infections (no PEI) were set to 100%. (B) Determination of PEI toxicity on HFFs after 10 days of recurrent administration. LDH activity in the supernatants and lysates of the HFF cells of the infection assay (A) was determined at 10 days of culture. Bars represent the mean of three individual experiments ± SD. (C) Impact of PEI (10 h p.i.) on initial HCMV infection in HFF cultures. Cells were infected with HCMV RV-ΔUS2-11_GFP (MOI, 0.03) or mock infected. At 10 h after infection, cells were washed with PBS. PEI at 16 nM was added to some of the cultures. At 48 h postinfection, GFP expression was measured as a means for determination of primary viral infection. Bars represent the mean of three individual experiments ± SD.
