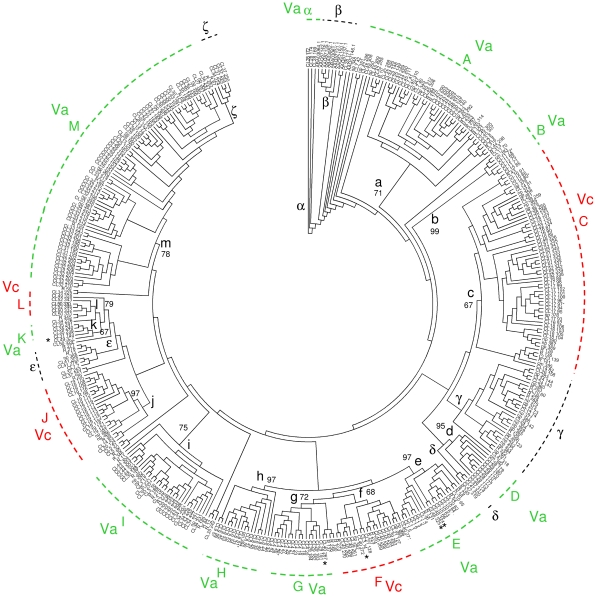
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of grapevine NBS-R genes.
The most abundant NBS-R gene classes were distributed among the different clades as follows: clades B, C, D, I and J included 80, 84, 88, 55, and 73% of CC-type genes, respectively; clade A included 70% of TIR-type genes; clades E, K, and M included 55, 60, and 59% of NBS-LRR genes, respectively; clades F, G, and H included 90, 63, and 67% of NBS-tr genes, respectively. Clades were assigned to Va (green) and Vc (red) genomes based only on clustered genes (Table 1 and Table S5). Asterisks mark clustered genes considered as exceptions to the genome assignment of a specific clade. Bootstrap values for clades A to M are expressed as percentages. The analysis included seven outgroup NBS-R genes of Pinus monticola [24].