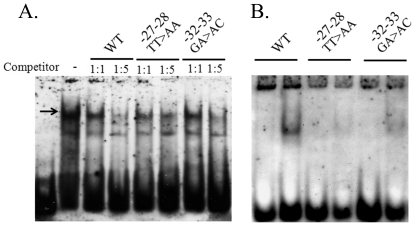
Figure 4. Mutations at the E2F/NF-e/c-Myb binding site affect binding of protein complexes to the vav1 promoter in vitro.
(A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) with Jurkat nuclear extracts was performed in the presence of digoxigenin-labeled probe spanning nucleotides −45 to 0 of vav1 promoter and containing E2F/NF-e/c-Myb and TCFα/PU.1/ELF1 binding sites (lil157-158; Table 3). The competition assay was performed with the labeled oligonucleotide and unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides with point mutations as indicated in Table 3 in molar ratio of 1∶1 and 1∶5. The arrow shows the position of the complex that demonstrates sensitivity to the introduced mutations. (B) EMSA performed with labeled oligonucleotide containing only E2F/NF-e/c-Myb binding site (lil 87-88; Table 3).