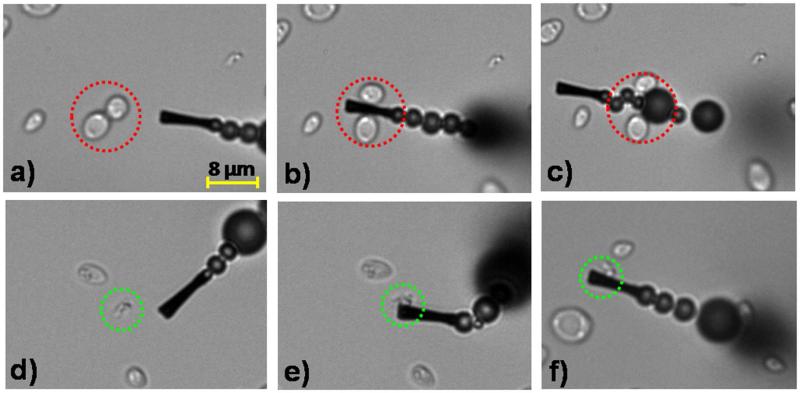
Figure 2.
Selective interaction between the ConA-functionalized microengines and the E. coli target bacteria in a fuel-enhanced and E. coli inoculated human urine sample. Time-lapse images - taken from Supporting Video S1A- before, during, and after interaction of the ConA-modified microengines with S. cerevisiae negative control (a–c, respectively) and E. coli target (d-f, respectively) cells. Urine samples are inoculated with E. coli (2.25×107 colony forming units (cfu/ml) or 4.5×104 cfu on the glass slide) and a 5-fold excess of S. cerevisiae and finally diluted 4 times in the glass slide to include the functionalized microengines and the fuel solutions (See Methods Section for additional details). Final fuel conditions: 7.5% (w/v) H2O2, 1.25% (w/v) Triton X-100. The E. coli and S. cerevisiae cells are accented by dashed green and red circles, respectively.