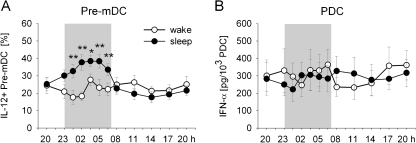
Fig. 3.
Sleep compared to nocturnal wakefulness selectively enhances the production of interleukin (IL)-12 by pre-myeloid dendritic cells (pre-mDC) which is important for the initiation of adaptive immune responses, whereas it does not influence the levels of interferon (IFN)-α that is released as an early response of the innate immune system upon viral infection. a The percentage of pre-mDC producing IL-12 measured after lipopolysaccharide stimulation of peripheral blood samples from healthy young men during a regular sleep–wake cycle (black circle) and during 24 h of continuous wakefulness (white circle). Analyses were performed by flow cytometry. b IFN-α production of plasmacytoid DC (pDC). Values indicate IFN-α concentrations measured by ELISA in whole blood samples after herpes simplex virus 1 stimulation, divided by the number of pDC. Means (±SEM) are shown. Shaded area indicates bed time. **p < .01, *p < .05 for pairwise comparison between conditions at single time points. Modified from Dimitrov et al. [33]