Fig. 2.
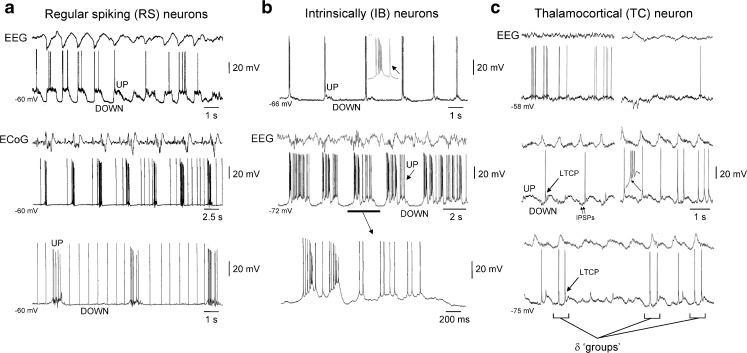
Reflection of the slow (<1 Hz) rhythm in neocortical and TC neurons in anaesthetised cats. a Top EEG and intracellular recording of an RS neuron in the cat neocortex during the slow rhythm. Note the presence of prominent UP and DOWN states, as indicated. Middle electrocorticogram (ECoG) recording and intracellular recording of a different neocortical RS neuron during the development of the slow rhythm (neuron recorded at a depth of 0.6 mm). In this neuron, DOWN states are characterised by low-frequency spontaneous firing. Bottom additional section of recording from the same neuron shown immediately above when the slow rhythm is fully developed. b Top intracellular recording of an IB neuron in the cat neocortex during the slow rhythm (recorded at a depth of 1.1 mm). Note how in this neuron, UP states start with a high-frequency burst of action potentials that is followed by little or no additional firing. Middle combined EEG and intracellular recording of a different IB neuron where UP states are initiated by a high-frequency burst that is followed by considerable additional firing (neuron recorded at a depth of 1.3 mm). The underlined section is enlarged below as indicated. c Top EEG and intracellular recording from a TC neuron in the ventrolateral nucleus during a period of low-amplitude EEG activity. Middle as EEG amplitude increases and the slow rhythm emerges, the TC neuron exhibits UP/DOWN states. Note how each UP state commences with an LTCP that often leads to a burst of action potentials and how the waveform of UP/DOWN states is well conserved from cycle to cycle. Note also the presence of rhythmic inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) during the DOWN state. Bottom upon further hyperpolarisation of the TC neuron, additional LTCPs are sometimes present during the DOWN state which are referred to as ‘grouped’ δ oscillations [15, 31, 33, 62, 73]. Top panel in a adapted from [1]. Middle and lower panels in a and all panels in b adapted from [61]. All panels in c adapted from [14]