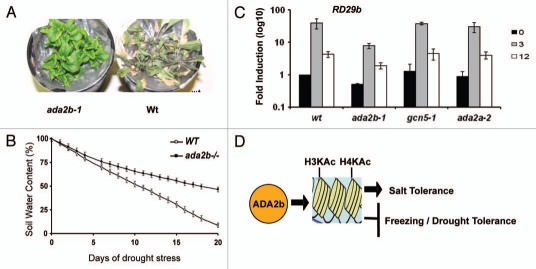
Figure 1.
ADA2b is a key regulator of abiotic stress. (A) ada2b-1 mutants are drought tolerant; photo was taken 20 d after water starvation. (B) Whole plant transpiration of wild type (white square) and ada2b-1 (black square) mutant plants. Changes in soil water content during drought stress is indicated. (C) The effect of ADA2a, ADA2b and GCN5 on salt-induced RD29b expression. Wild-type Ws, ada2a-1, ada2a-2 and gcn5-1 plants were subjected to salt stress (100 mM NaCl) for various time as indicated. RNA were isolated from whole seedling and real-time Reverse Transcription PCR was performed using specific primers for RD29b. Fold induction of these genes after exposure to 100 mM NaCl were calculated by normalizing values from salt-treated plants with those from untreated samples. Values are presented on a logarithmic scale. For each mutant and wild-type plants, triplicate samples in each experiment were assayed twice. Three independent experiments were performed, error bars represent SE where n = 4. (D) Schematic representation of ADA2b function. ADA2b promotes histone acetyaltion in salt-induced genes and confers salt tolerance whereas it represses freezing and drought tolerant in Arabidopsis.