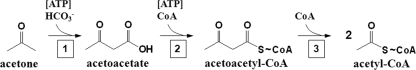
Fig 2.
Proposed catabolic pathway of acetone. Acetone is carboxylated to acetoacetate (reaction 1) by acetone carboxylase. Activation of acetoacetate to acetoacetyl-CoA (reaction 2) may be catalyzed by either a CoA ligase or a CoA transferase. Reactions 1 and 2 are proposed to be ATP dependent. Acetoacetyl-CoA is then thiolytically cleaved (reaction 3) by a thiolase to form 2 acetyl-CoA.