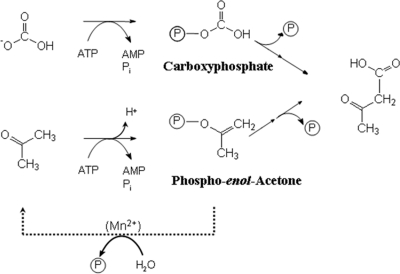
Fig 6.
Proposed catalytic mechanism of acetone carboxylation catalyzed by acetone carboxylase. Bicarbonate is activated to carboxyphosphate by hydrolysis of 1 ATP, while a second ATP is hydrolyzed to activate acetone to phosphoenol acetone. This activated intermediate can undergo hydrolysis in the absence of bicarbonate, which can be measured as decoupled ATPase activity. This activity appears to be stimulated by Mn2+.