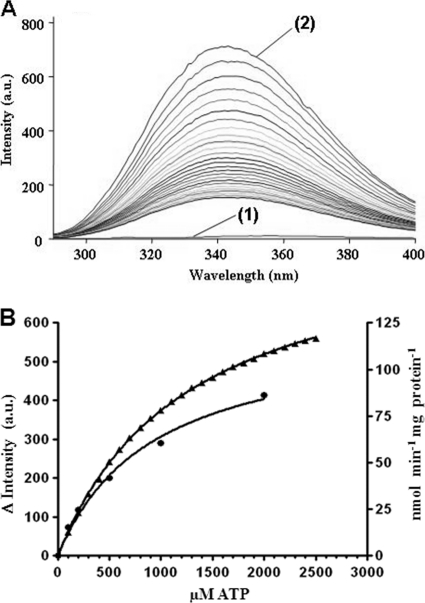
Fig 7.
ATP kinetics of purified acetone carboxylase. (A) Changes in the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of Acx upon binding of ATP (excitation wavelength, 280 nm). Emission spectra of a buffer control [labeled (1)] and 500 nM Acx [labeled (2)] are shown along with emission spectra of Acx with increasing ATP concentrations (0.1 to 2.5 mM). (B) Kinetics of ATP binding (triangles) and enzyme activity (circles) of acetone carboxylase. ATP binding was determined as the concentration-dependent change in endogenous fluorescence at 343 nm in the absence of acetone, calculated from the data shown in panel A. ATP dependence of enzyme kinetics was determined by determining the [14C]bicarbonate incorporation (assay I) into reaction products. Standard deviations of triple assays were smaller than the graph symbols used.