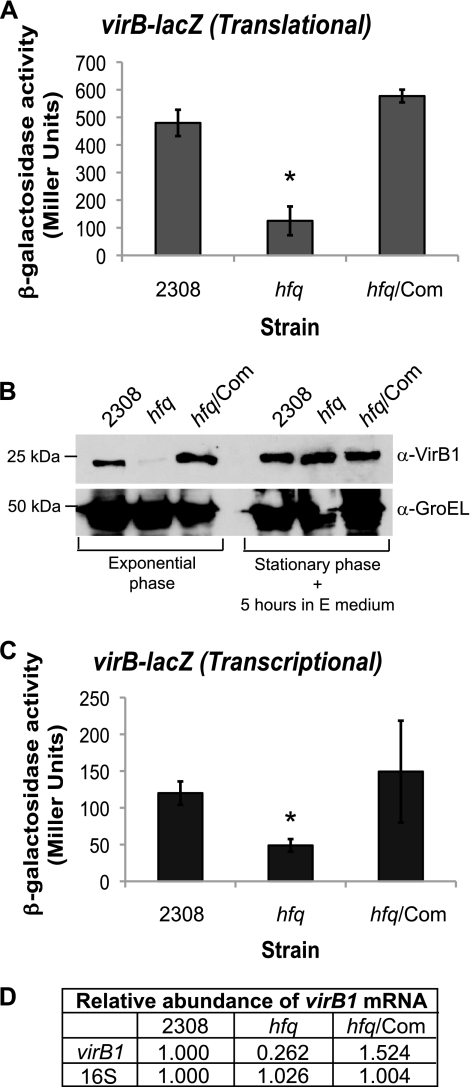
Fig 1.
Hfq is required for maximal expression of the VirB system. Plasmid constructs pC3005 (A) and pC3003 (C) (Table 2) were transformed into B. abortus 2308, the hfq isogenic mutant (hfq), and the hfq mutant strain expressing hfq from a plasmid (hfq/Com), and following cultivation in low-pH (pH 4.5) defined medium, β-galactosidase activity was assessed. The asterisk denotes a statistically significant difference between the β-galactosidase activities of parental strain 2308 and the hfq mutant strain (P < 0.01). (B) Immunoblot analysis of VirB1 protein levels. Brucella strains were cultivated in low-pH minimal E medium. GroEL levels are shown as a protein loading control, and molecular weight markers are shown to the left. (D) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of virB1 transcript levels. Brucella strains were grown in low-pH (pH 4.5) defined medium, and total RNA was isolated. Oligonucleotide primers specific for virB1 or 16S rRNA were used to amplify the target genes by PCR, and quantification of the amplified DNA fragments was performed using SYBR green incorporation. The values represent the relative abundances of specific mRNAs, with the level of mRNA from parental strain 2308 designated 1.000.