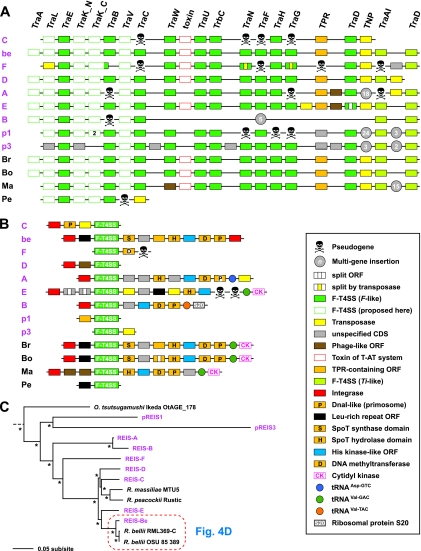
Fig 5.
Characteristics of the RAGE. (A and B) Schema of gene organization within nine complete (or nearly complete) RAGEs in the REIS genome (pink) and their comparison to the single-copy RAGEs encoded in four other Rickettsia genomes: Br, R. bellii strain RML369-C; Bo, R. bellii strain OSU 85-389; Ma, R. massiliae strain MTU5; Pe, R. peacockii strain Rustic. The genome coordinates of the REIS RAGEs are illustrated in Fig. 1B. Gene color and symbols are described in the inset. (A) Illustration of the RAGE-encoded F-like type IV secretion system (F-T4SS) genes. (B) Illustration of the regions flanking the RAGE F-T4SS genes, including several proposed tRNA insertion sites. (C) Phylogeny estimation of the RAGE genes illustrated in panel A. Nineteen protein families were included in the analysis (excluding TraA pilins and the conserved transposase flanked by TraDF and TraAITi), with pseudogenes not included. Branch support (posterior probabilities) is from Bayesian analysis (see the text for details). Phylogeny estimates of the individual RAGE genes are provided in Fig. S10 in the supplemental material.