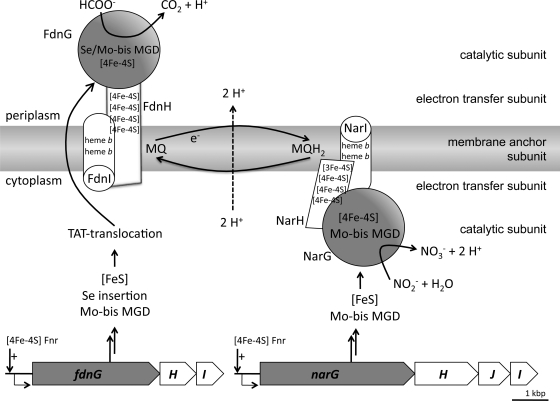
Fig 1.
Schematic representations of the organization of the formate dehydrogenase N and nitrate reductase enzymes in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Shown are the FNR-regulated structural gene operons for Fdh-N (fdnGHI) and Nar (narGHJI) and the steps required from protein synthesis via cofactor insertion ([Fe-S] cluster, selenocysteine [Se], molybdo-bis-molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide [Mo-bis-MGD]) to Tat-dependent membrane transport for Fdh-N. The membrane anchor subunits FdnI and NarI also contain heme b cofactors, the electron transfer subunits FdnH and NarH have several [FeS] clusters, and the catalytic subunits FdnG and NarG have Mo-bis MGD, [4Fe-4S] and Se (only FdnG). The reaction catalyzed by each enzyme and the connecting menaquinone (MQ)-menaquinol (MQH2)-based redox loop is shown. e−, electron.