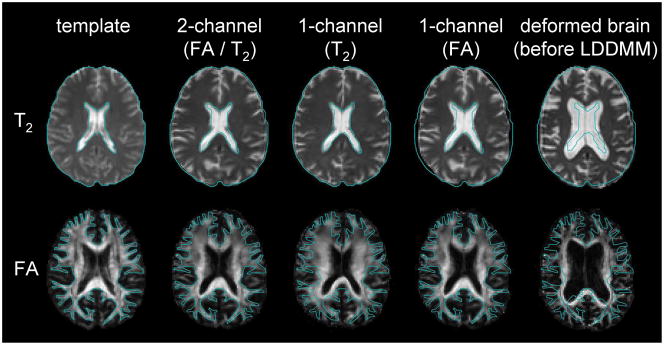
Fig. 5.
The efficacy of dual-channel image registration. The blue line indicates the boundary of the brain (T2) and the white matter (FA) of the template. T2 and DTI carry contrasts in a spatially complementary manner. In this example, the atrophic brain with substantial ventricular enlargement is normalized to the template. When T2 is used to drive the transformation, the brain boundary and the ventricle of the patient become very similar to those of the template (T2), but the white matter structure is not similar to that of the template. If only the FA map is used, the white matter shape becomes very similar to the template, but the brain boundary is not matched (FA). By using both contrasts, the registration quality of the entire brain drastically improves (FA/T2). (From Ceritoglu C, Oishi K, Li X et al. Multi-contrast large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping for diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage 2009;47:618; with permission.)